What is the meaning of photovoltaic power plants
Photovoltaic power plants are facilities that utilize the photovoltaic effect to convert sunlight into electricity. This is achieved through the use of solar panels, which are made up of numerous solar cells that absorb sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity. This electricity can then be converted into alternating current (AC) and used to power homes, businesses, and other applications.
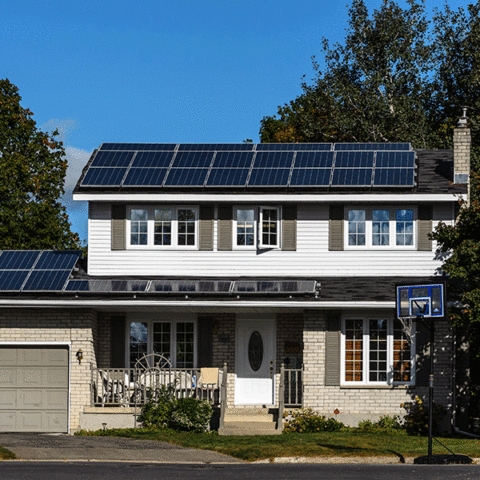
How do photovoltaic power plants work?
1. Solar panels
The core component of a photovoltaic power plant is the solar panel. These panels are typically made from silicon-based materials that have the ability to generate an electric current when exposed to sunlight.
2. Inverter systems
Once the solar panels have converted sunlight into DC electricity, inverter systems are used to convert the DC electricity into AC electricity, which is the standard form of electricity used to power buildings and appliances.
3. Grid connection
Photovoltaic power plants are often connected to the electrical grid, allowing them to feed excess electricity back into the grid for use by others. This can also enable the plant to draw electricity from the grid when sunlight is not available.

4. Monitoring and control systems
Photovoltaic power plants are equipped with sophisticated monitoring and control systems that allow operators to track the performance of the plant, adjust system settings, and detect any issues that may arise.
5. Environmental impact
One of the key benefits of photovoltaic power plants is their minimal environmental impact. By harnessing the power of the sun, these plants produce clean, renewable energy without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants.
Conclusion
Photovoltaic power plants represent a sustainable and efficient way to generate electricity, helping to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. As technology continues to advance, these plants are expected to play an increasingly important role in the global energy landscape.

