Photovoltaic materials are essential components of solar cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. The effectiveness of a photovoltaic material greatly determines the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of a solar cell. Therefore, it is crucial to use high-quality materials in the manufacturing of solar panels. In this article, we will explore what makes a good photovoltaic material and the key characteristics to consider when selecting materials for solar cell production.

Key Characteristics of a Good Photovoltaic Material
1. Optimal Bandgap
The bandgap of a material is a crucial factor in determining its efficiency in converting solar energy into electricity. An ideal photovoltaic material should have a bandgap that allows it to absorb a broad spectrum of sunlight, including both visible and infrared light. Materials with a narrow bandgap tend to absorb only a limited range of light, while materials with a wide bandgap can only absorb high-energy photons. Therefore, a good photovoltaic material should have an optimal bandgap to maximize energy conversion.2. High Carrier Mobility
Carrier mobility refers to the ability of charge carriers (electrons and holes) to move through the material. In photovoltaic materials, high carrier mobility leads to efficient charge transport, resulting in higher electrical conductivity and better overall device performance. Therefore, a good photovoltaic material should have high carrier mobility to ensure effective charge carrier transport and collection.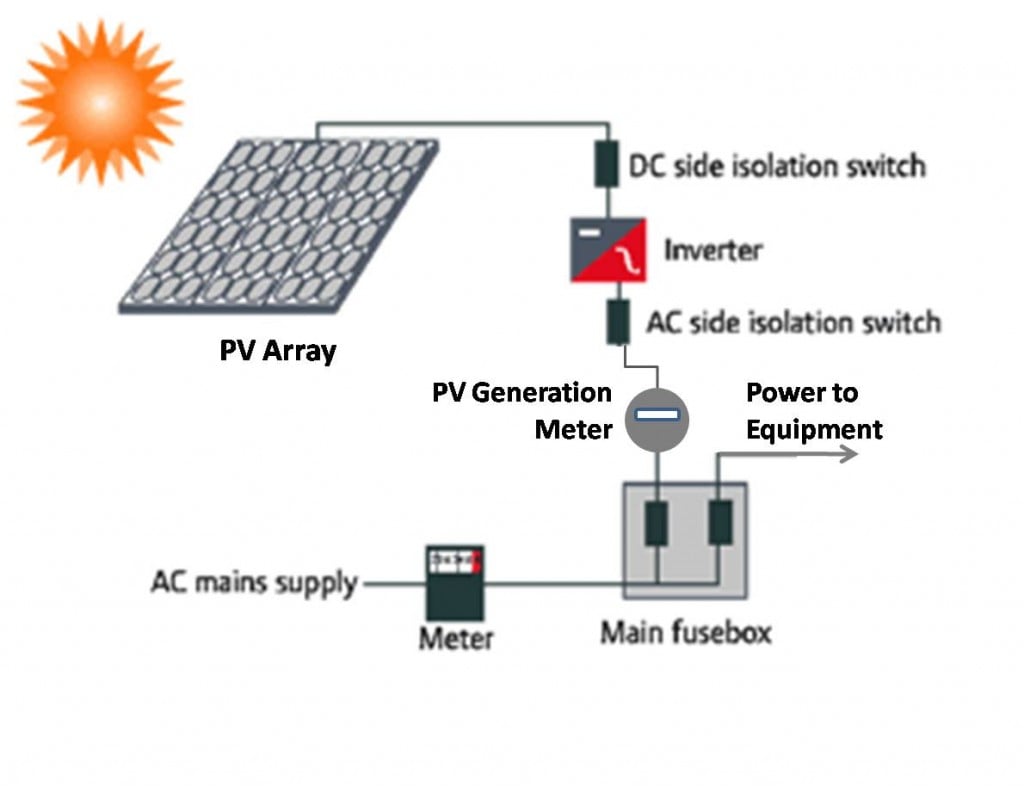
3. Stability and Durability
Solar cells are expected to have a long operational lifetime, often spanning several decades. As such, it is important for photovoltaic materials to exhibit stability and durability under prolonged exposure to sunlight and environmental factors. Materials that are susceptible to degradation or corrosion over time are not suitable for solar cell applications. Good photovoltaic materials should be able to maintain their performance and structural integrity over extended periods of use.Types of Photovoltaic Materials
1. Crystalline Silicon
Crystalline silicon is currently the most widely used material in commercial solar cells due to its abundance and proven performance. It offers high efficiency and long-term stability, making it a top choice for solar panel manufacturers. However, the production of crystalline silicon solar cells can be energy-intensive and costly.2. Thin-Film Materials
Thin-film photovoltaic materials, such as cadmium telluride (CdTe) and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), offer the advantage of being lightweight and flexible. They can be deposited on various substrates, allowing for the potential development of low-cost, high-efficiency solar panels. However, their performance and stability may vary, and their toxicity is a concern for some applications.3. Perovskite Materials
Perovskite solar cells have garnered significant attention in recent years due to their rapid efficiency improvements and potential for low-cost production. These materials exhibit high absorption coefficients and tunable bandgaps, making them promising candidates for next-generation solar cells. However, their stability and long-term performance under real-world conditions remain areas of active research and development.In conclusion, a good photovoltaic material should possess optimal bandgap, high carrier mobility, and stability/durability. While crystalline silicon remains the dominant material in the solar industry, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on thin-film and perovskite materials to further improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar cells. By continuously advancing the properties and performance of photovoltaic materials, the solar energy industry can contribute to a more sustainable and renewable energy future.

