What Part of Light Do Photovoltaic Cells Convert?
Introduction
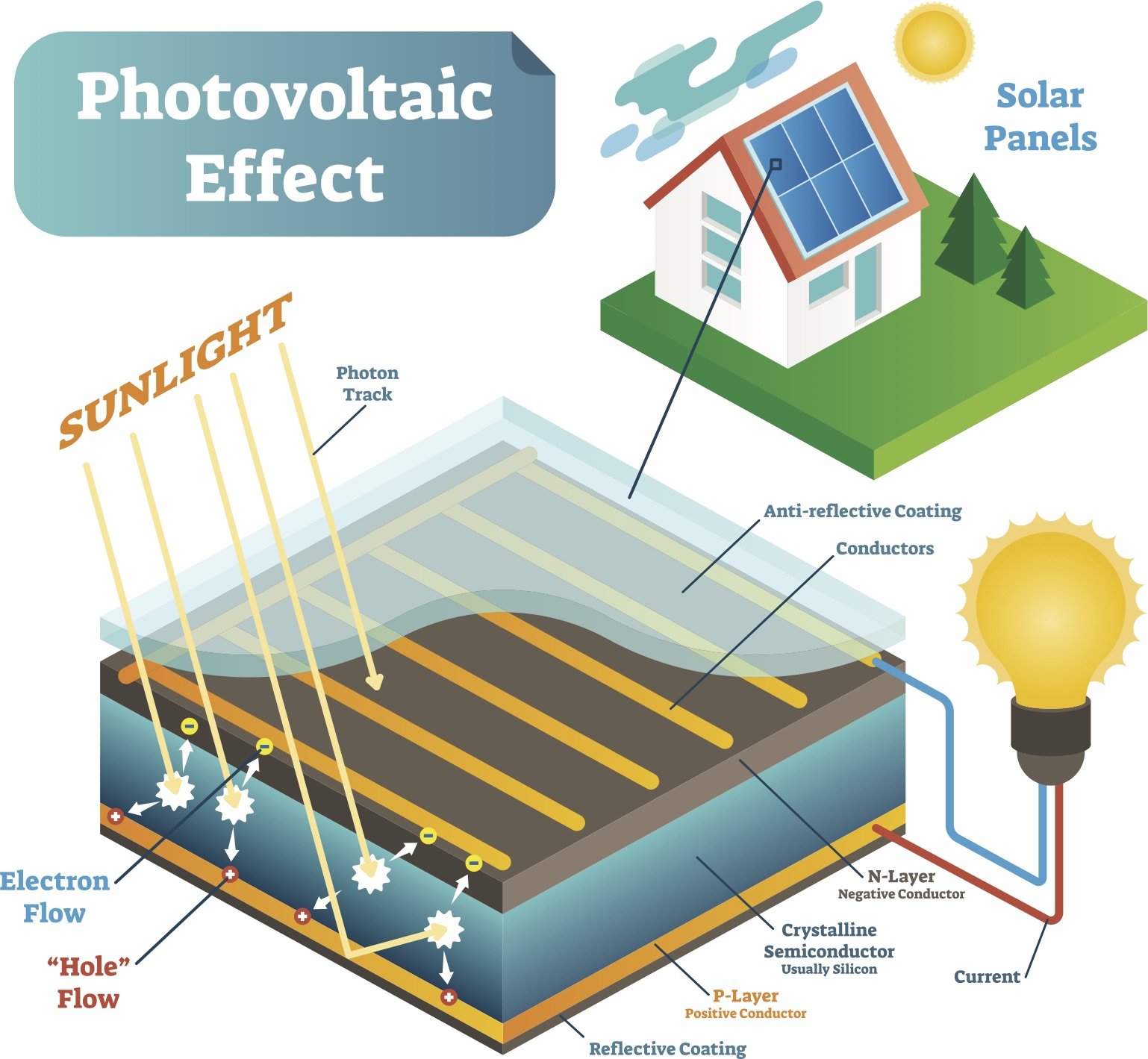
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert light into electricity. These cells are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, which can absorb light and convert it into an electrical current. However, not all parts of light are equally effective at producing electricity in photovoltaic cells.
How Photovoltaic Cells Work
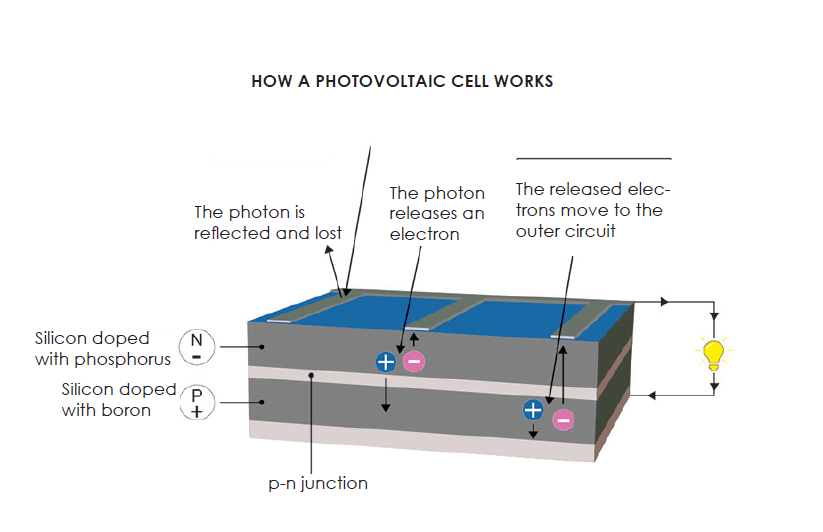
When photons, which are particles of light, strike the surface of a photovoltaic cell, they can be absorbed by the semiconductor material. This absorption causes the semiconductor to release electrons, which then flow through the material to produce an electrical current. The most efficient photovoltaic cells are able to capture a wide range of light wavelengths, from ultraviolet to infrared, and convert them into electricity.
The Visible Light Spectrum
The visible light spectrum is the range of light wavelengths that are visible to the human eye, and it includes colors from violet to red. Photovoltaic cells are most efficient at converting light in the visible spectrum, particularly in the blue and red wavelengths. Blue light has higher energy photons, which can release more electrons when absorbed by the semiconductor material, while red light has slightly lower energy photons but still contributes to electricity production.
Blue Light
Blue light, with wavelengths of around 450-495 nanometers, is one of the most effective parts of the visible light spectrum at producing electricity in photovoltaic cells. This is because blue light has higher energy photons, which can release more electrons when absorbed by the semiconductor material.
Red Light
Red light, with wavelengths of around 620-750 nanometers, is also effective at producing electricity in photovoltaic cells. While red light has slightly lower energy photons compared to blue light, it still contributes to electricity production and is an important part of the overall light spectrum that is converted by photovoltaic cells.
Infrared and Ultraviolet Light
Infrared light, with wavelengths longer than red light, and ultraviolet light, with wavelengths shorter than blue light, are less effective at producing electricity in photovoltaic cells. While some advanced photovoltaic cell designs are able to capture a small portion of these light wavelengths, they are not as efficient at converting infrared and ultraviolet light into electricity compared to the visible light spectrum.
Conclusion
In conclusion, photovoltaic cells are most efficient at converting light in the visible spectrum, particularly in the blue and red wavelengths. These parts of the light spectrum have higher energy photons, which can release more electrons when absorbed by the semiconductor material, leading to increased electricity production. While infrared and ultraviolet light can also contribute to electricity generation, they are less effective at producing electricity in photovoltaic cells compared to the visible light spectrum.



