Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are a key component in solar panel technology. These cells are responsible for converting light into electricity, making them an essential part of harnessing solar energy. But how exactly do photovoltaic cells work to generate electricity from sunlight? Let’s take a closer look at the part of the photovoltaic cell that is responsible for this crucial conversion process.
How do photovoltaic cells work?
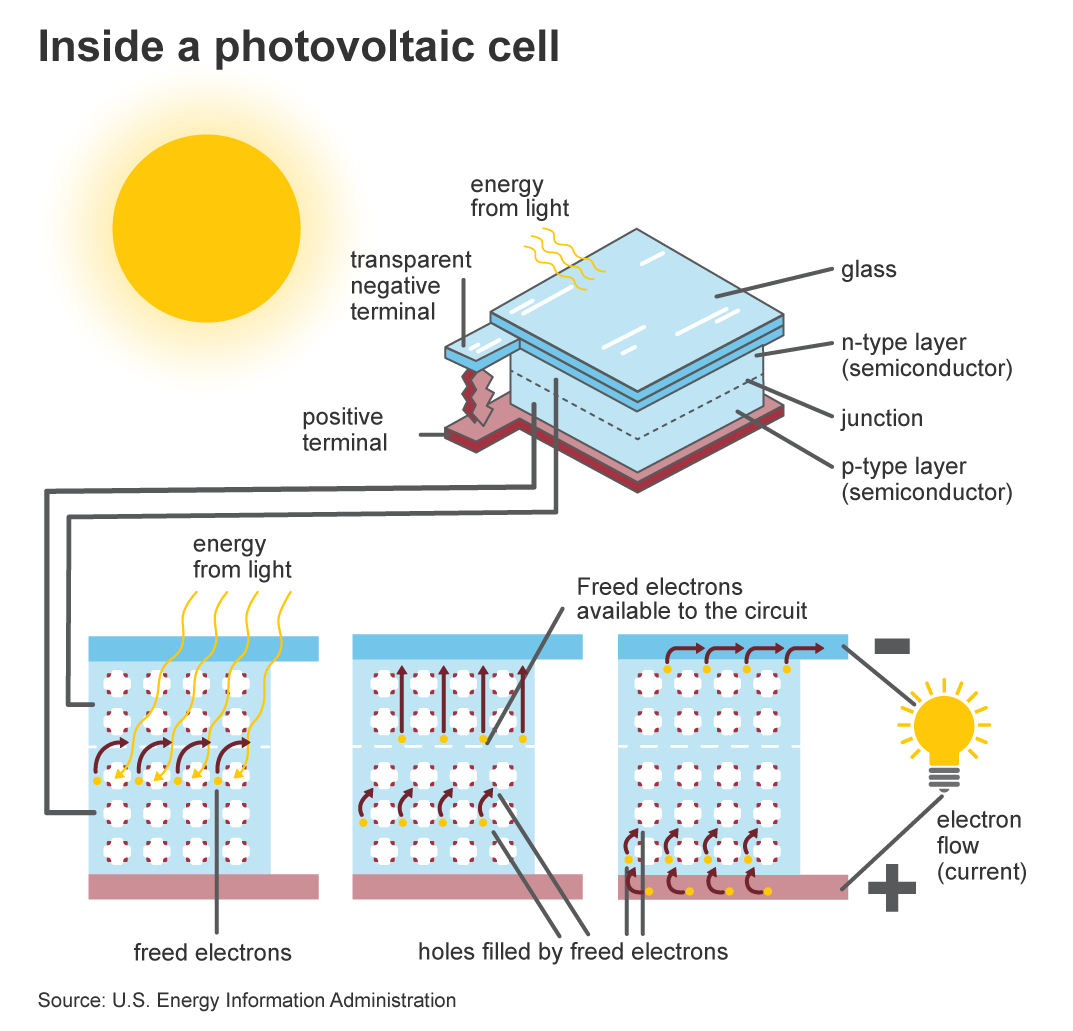
Photovoltaic cells are made of semiconductor materials, typically silicon, that are specially treated to create a positive/negative junction. When photons of light strike the surface of the cell, they can knock electrons loose from their atoms. This creates a flow of electricity, which can then be captured and used to power electrical devices.The role of the semiconductor material
The semiconductor material in a photovoltaic cell is the key component that is responsible for converting light to electricity. When photons strike the surface of the semiconductor, they transfer their energy to electrons in the material, causing them to become free and mobile. The movement of these electrons creates an electric current, which can then be harnessed for various applications.The importance of the positive/negative junction
In addition to the semiconductor material, the positive/negative junction within the cell is also crucial for the conversion of light to electricity. This junction creates an electric field within the cell, which helps to separate the newly freed electrons from the positively charged holes they leave behind. This separation allows for the flow of electricity to be maintained, thus enabling the cell to generate a usable electrical current.
The generation of electrical current
Once the electrons are set into motion by the photons of light and the electric field within the cell, they can be captured by metal contacts on the cell’s surface and channeled into an external circuit. This flow of electrons constitutes the generation of an electrical current, which can then be used to power a wide range of devices and appliances.In conclusion, the semiconductor material and the positive/negative junction within a photovoltaic cell are the key components responsible for converting light into electricity. By harnessing the energy of photons and creating an electric current, these cells play a critical role in the generation of solar power. As solar energy continues to gain traction as a clean and sustainable source of power, the technology behind photovoltaic cells will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in our energy landscape.

