What’s the Carbon Footprint of Photovoltaic Electricity?
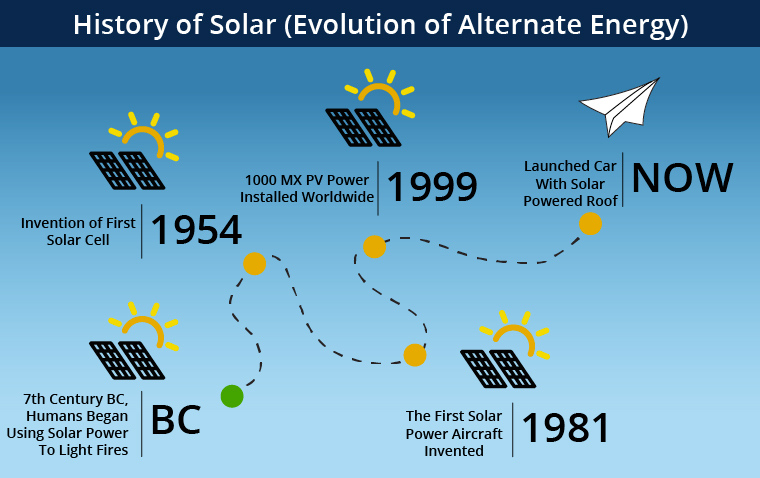
Understanding the Carbon Footprint of Photovoltaic Electricity
Photovoltaic electricity, or solar power, is a renewable energy source that generates electricity from sunlight using photovoltaic cells. It is considered one of the cleanest forms of energy as it produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions during its operation. However, the carbon footprint of photovoltaic electricity encompasses the entire life cycle of the technology, from the manufacturing of solar panels to their disposal.
What is a Carbon Footprint?
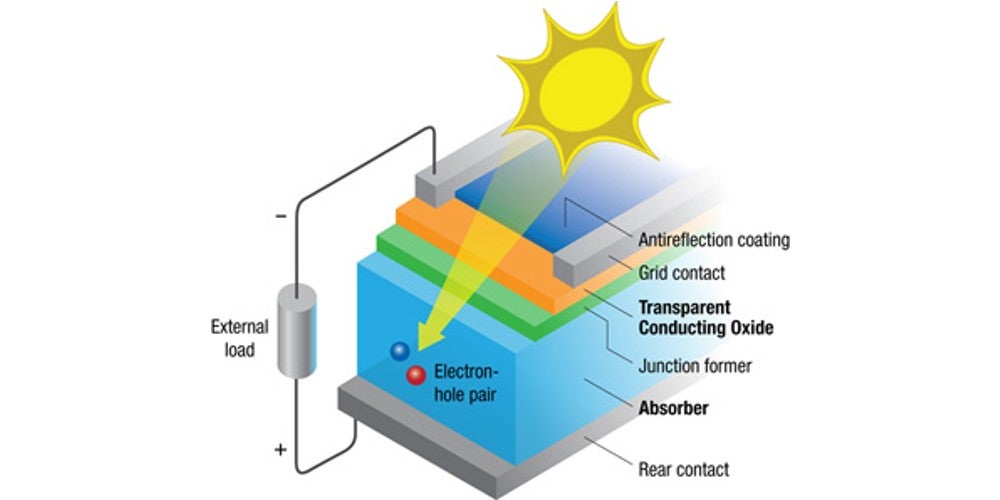
A carbon footprint is the total amount of greenhouse gases, specifically carbon dioxide, that are emitted directly or indirectly by an individual, organization, product, or service. It is measured in units of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) and provides a comprehensive assessment of the environmental impact of a specific activity or product.
The Manufacturing Process
The carbon footprint of photovoltaic electricity begins with the manufacturing of solar panels, which involves the use of various materials and chemicals. The production of solar panels typically requires the mining and processing of raw materials such as silicon, cadmium, tellurium, and gallium. These processes contribute to carbon emissions and other environmental impacts.
Installation and Operation
Once solar panels are manufactured, their installation and operation produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions in comparison to traditional fossil fuel-based electricity generation. Solar panels have a long lifespan and require little maintenance, resulting in low ongoing carbon emissions. Additionally, the electricity generated by photovoltaic systems offsets the emissions that would have been produced by conventional power plants.
End-of-Life Considerations
When solar panels reach the end of their life, proper disposal or recycling is essential to mitigate their carbon footprint. Currently, most solar panels end up in landfills, and the recycling infrastructure for solar panel components is still in its infancy. Efforts to improve the recycling and disposal of solar panels are crucial in minimizing their environmental impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the carbon footprint of photovoltaic electricity includes emissions from the manufacturing process and end-of-life considerations, the overall impact is significantly lower than that of traditional energy sources. The continued advancement of solar technology and sustainable practices in the industry will further reduce the carbon footprint of photovoltaic electricity, making it an increasingly attractive and environmentally friendly energy option.
By understanding and addressing the carbon footprint of photovoltaic electricity, we can make informed decisions about our energy choices and contribute to a more sustainable future.

