When to Use Photoconductive or Photovoltaic Mode
Photoconductive and photovoltaic modes are two different ways in which materials can interact with light to generate an electrical current. Understanding when to use each mode is important for maximizing the performance of electronic devices and systems. In this article, we will discuss the differences between photoconductive and photovoltaic modes and when to use each one.
Photoconductive Mode
In the photoconductive mode, the electrical conductivity of a material is increased when exposed to light. This occurs because the energy of the incident photons is enough to promote electrons from the valence band to the conduction band, creating additional charge carriers and increasing conductivity. Photoconductive materials are commonly used in devices such as photodetectors, solar cells, and photoconductors.When to Use Photoconductive Mode
1. When high sensitivity to light is required: Photoconductive materials offer high sensitivity to light, making them suitable for applications where detecting low levels of light is necessary, such as in imaging sensors and night vision devices.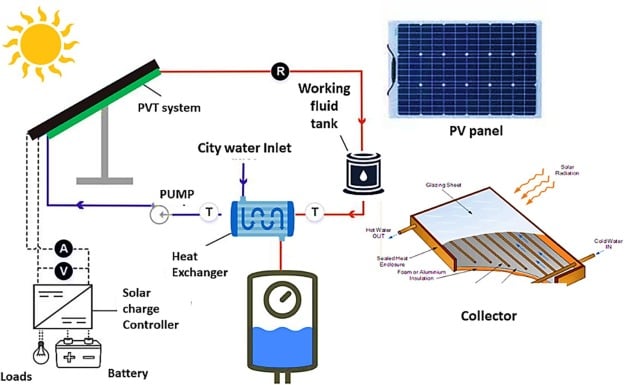
2. When fast response time is important: Photoconductive materials typically exhibit fast response times to changes in light levels, making them suitable for applications where rapid detection of light is required, such as in optical communication systems.
3. When a variable electrical response to light is needed: Photoconductive materials can provide a variable electrical response to changes in light intensity, making them useful for applications where the electrical output needs to be proportional to the incident light.
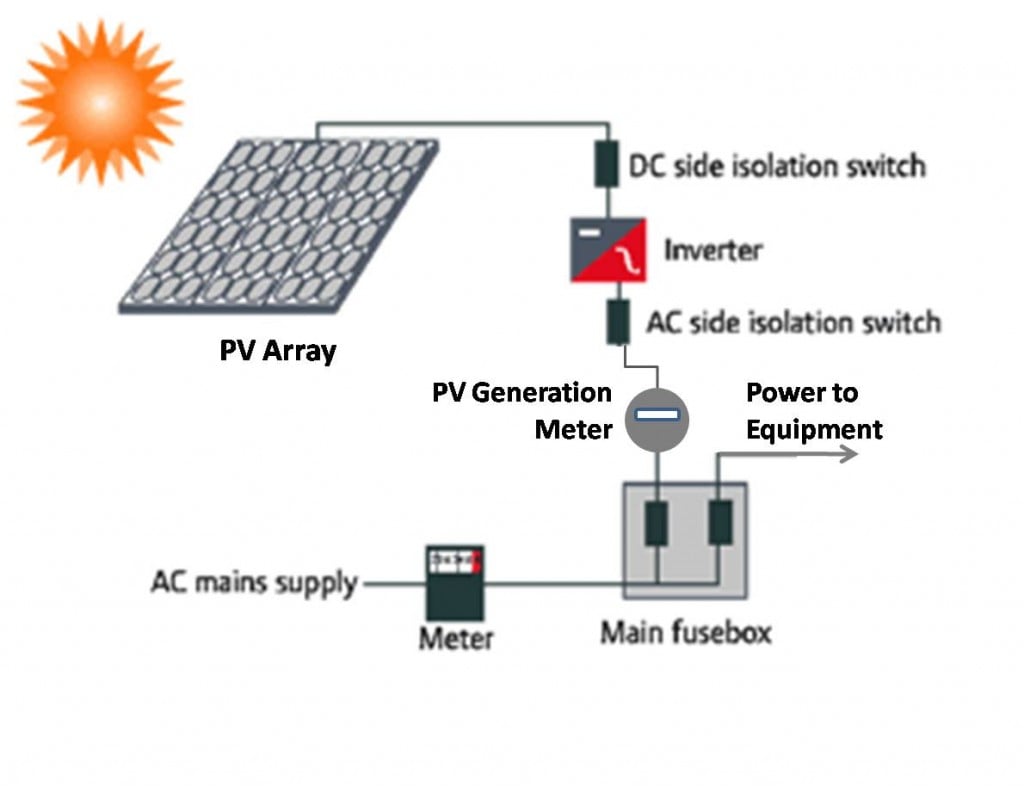
Photovoltaic Mode
In the photovoltaic mode, a material generates a voltage and current when exposed to light, without the need for an external bias. This occurs due to the creation of a built-in electric field within the material, which separates the photo-generated electrons and holes, leading to the generation of a photovoltage and photocurrent. Photovoltaic materials are commonly used in devices such as solar cells and photodiodes.When to Use Photovoltaic Mode
1. When energy conversion is the primary goal: Photovoltaic materials are highly efficient at converting light energy into electrical energy, making them ideal for applications such as solar panels and energy harvesting devices.2. When a steady electrical output is required: Photovoltaic materials can provide a steady electrical output, making them suitable for applications where a continuous and stable power supply is needed, such as in off-grid power systems.
3. When simplicity and reliability are important: Photovoltaic materials operate without the need for external bias or complex circuitry, making them easy to integrate into electronic systems and reliable in operation.
In conclusion, the decision to use photoconductive or photovoltaic mode depends on the specific requirements of the application. Photoconductive mode is best suited for high sensitivity, fast response, and variable electrical response to light, while photovoltaic mode is ideal for energy conversion, steady electrical output, and simplicity and reliability. By understanding the differences between these modes and their respective advantages, engineers and designers can make informed choices when selecting materials for light-sensitive electronic devices and systems.

