Which Areas Need Grid-Tied Battery Storage Systems
The Benefits of Grid-Tied Battery Storage Systems
Residential Areas
In residential areas, grid-tied battery storage systems can provide homeowners with backup power during outages and help reduce their electricity bills by storing excess energy generated from solar panels or other renewable sources.
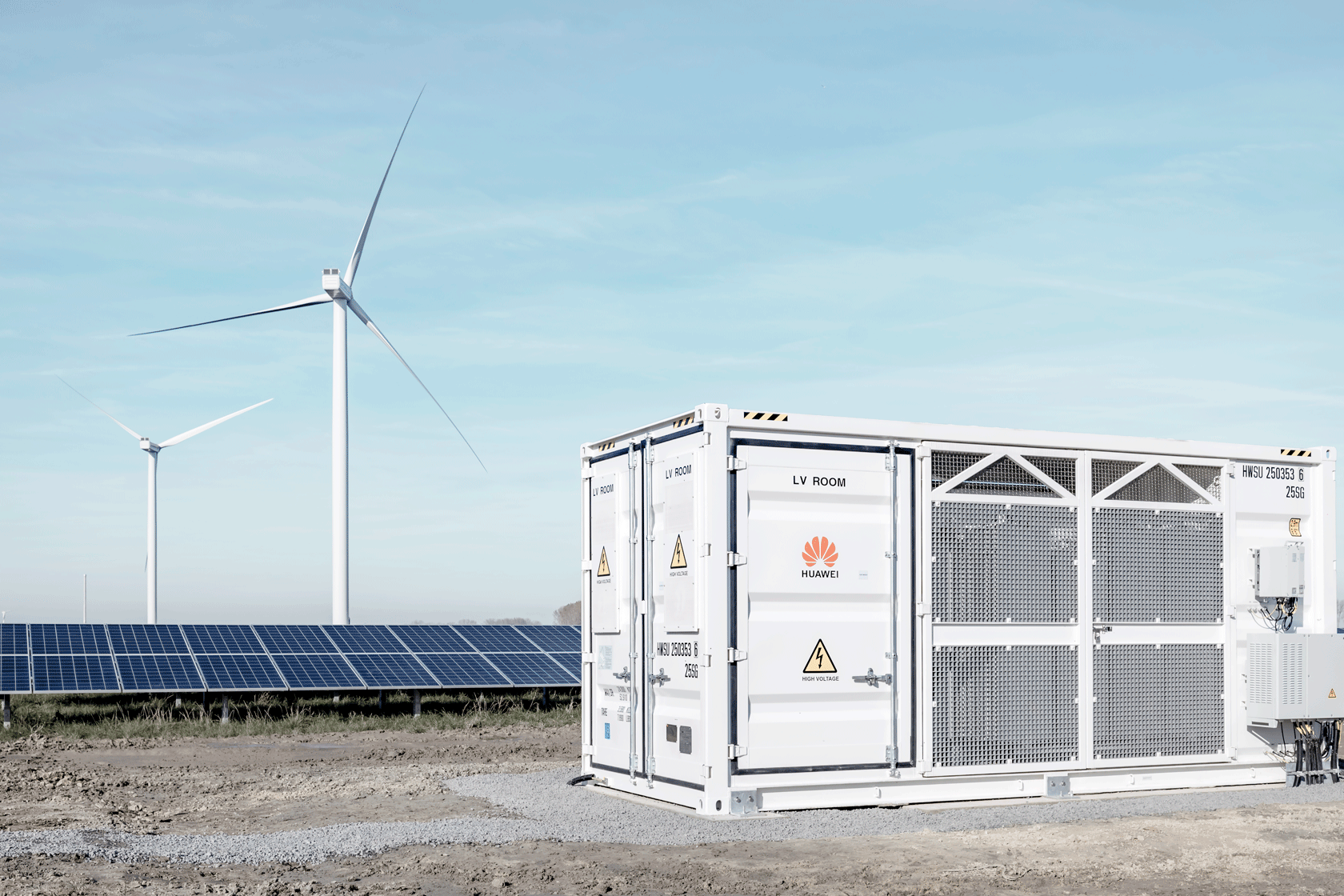
Commercial and Industrial Areas
Businesses and industries can benefit from grid-tied battery storage systems by reducing their reliance on the grid during peak demand times and lowering their overall energy costs.
Rural and Remote Areas
Rural and remote areas that are not connected to the main power grid can greatly benefit from grid-tied battery storage systems, as they can provide a reliable and sustainable energy source.
Challenges for Implementing Grid-Tied Battery Storage Systems
Regulatory Barriers
One of the main challenges for implementing grid-tied battery storage systems is navigating regulatory barriers, as different areas may have varying policies and regulations regarding energy storage systems.
Initial Cost
The initial cost of installing a grid-tied battery storage system can be a barrier for many individuals and businesses, although the long-term savings and benefits often outweigh the upfront investment.
Technology and Integration
The integration of grid-tied battery storage systems with existing energy infrastructure and technology can be complex and require expertise to ensure seamless operations.
Environmental Impact
When considering grid-tied battery storage systems, it is important to assess the potential environmental impact, including the sourcing and disposal of batteries, to ensure a sustainable solution.
Capacity and Demand
Matching the capacity of grid-tied battery storage systems with the energy demand of the area is crucial for maximizing the benefits and reliability of the system.
Conclusion
Overall, grid-tied battery storage systems have the potential to benefit a wide range of areas, from residential to remote locations, by providing backup power, reducing energy costs, and promoting sustainability. Overcoming challenges such as regulatory barriers, initial costs, and technology integration is essential for the widespread adoption of these systems. As technology continues to advance and awareness grows, the implementation of grid-tied battery storage systems will likely become more common in various areas.




