The Photovoltaic Effect: A Brief History of Its Discovery
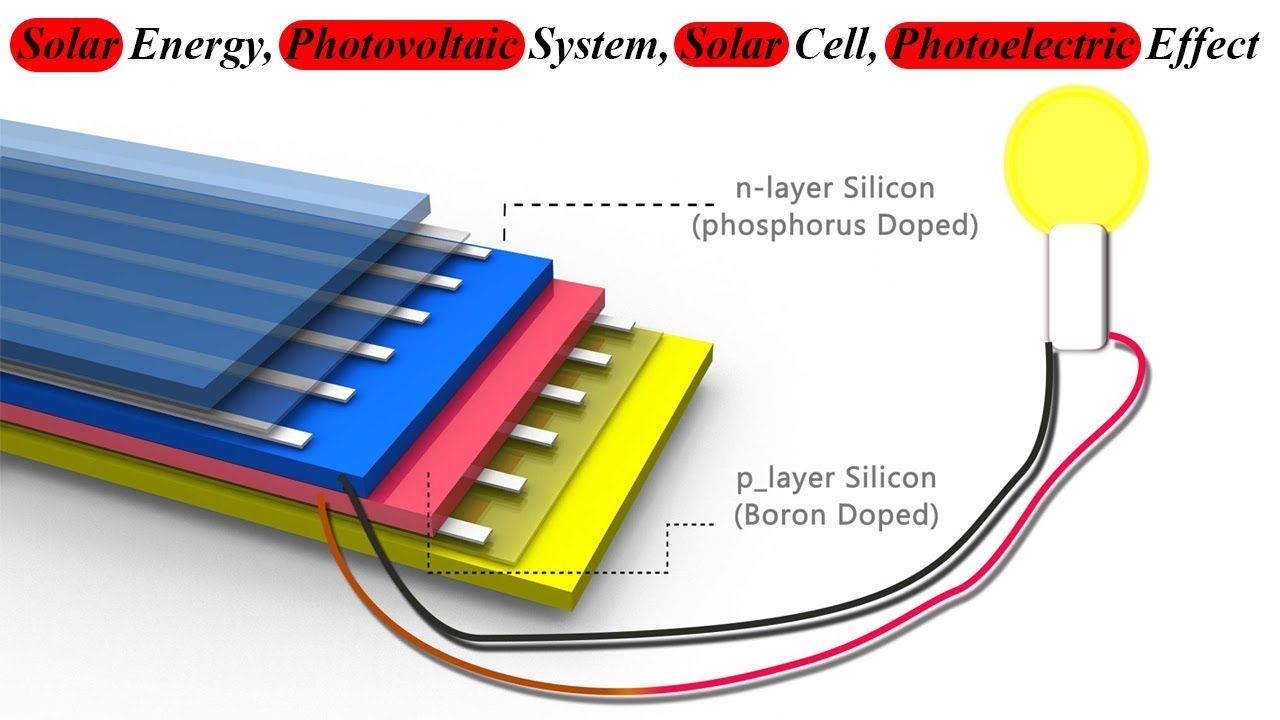
The photovoltaic effect, which refers to the creation of a voltage when light is absorbed by a material, is the principle behind solar panels and solar cells. This phenomenon has been known for over a century, and its discovery has revolutionized the way we harness sunlight to generate electricity. In this article, we will explore the history of the photovoltaic effect and the individuals who played a crucial role in its discovery.
The Beginnings of Photovoltaic Exploration
The photovoltaic effect was first discovered in 1839 by French physicist Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel. At the age of 19, Becquerel was conducting experiments with electrolytic cells when he observed that the production of electricity increased when the cells were exposed to light. This led him to conclude that light could be used to generate electric current, laying the foundation for the study of photovoltaics.Key Figures in the Development of Photovoltaics
Over the years, several scientists and researchers have made significant contributions to our understanding of the photovoltaic effect. One of the most notable figures is Albert Einstein, who in 1905 published a paper on the photoelectric effect, which explained the interaction of light and electrons in a solid material. This work earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921 and laid the groundwork for the development of solar cells.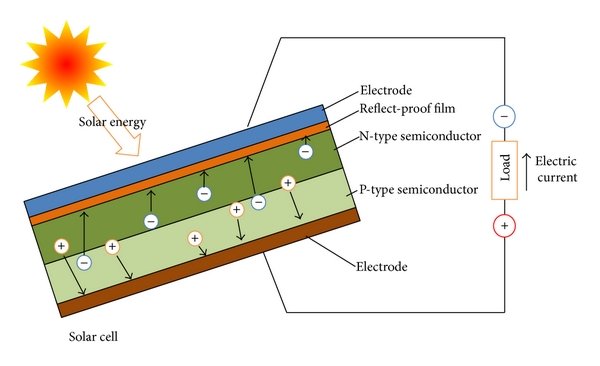
Another pioneering figure in the field of photovoltaics is Russell Ohl, an American physicist who is credited with the invention of the first silicon solar cell in 1941. Ohl’s discovery of the p-n junction, a crucial component of modern solar cells, paved the way for the practical application of solar energy technology.

