How Do Photovoltaic Cells Work?
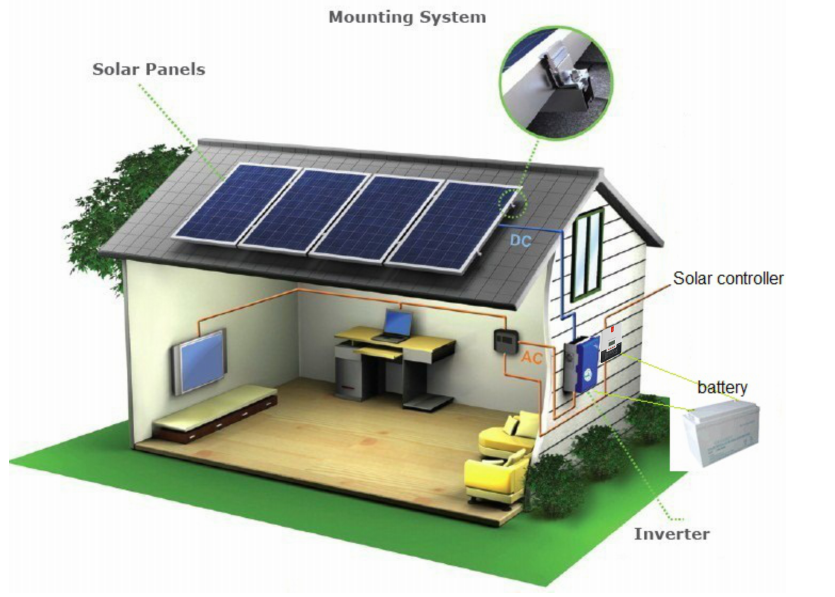
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are a critical component of solar panels. These cells have the remarkable ability to convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. But how do photovoltaic cells actually work?
1. Composition of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are typically made from layers of semiconductor materials, such as silicon. These materials have a special property that allows them to absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons. This process creates an electric current.
1.1. Semiconductor Material
The semiconductor material used in photovoltaic cells is usually doped with other elements to create a p-n junction. This junction creates an electric field that helps to separate the electrons and holes produced by the absorption of sunlight.
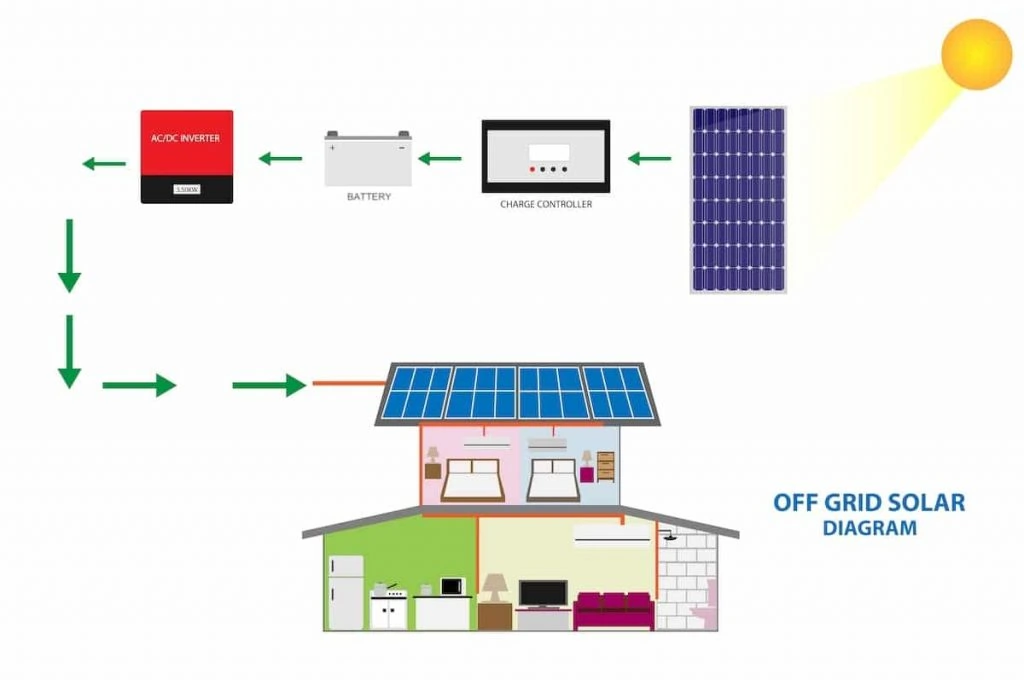
1.2. Metal Contacts
Metal contacts are attached to the top and bottom of the semiconductor material to collect the electrons and holes that are separated by the electric field. These metal contacts form the electrical circuit of the photovoltaic cell.
2. The Photovoltaic Effect
When sunlight hits the surface of a photovoltaic cell, its energy is absorbed by the semiconductor material. The photons from the sunlight release electrons and create a flow of electricity. This is known as the photovoltaic effect.
2.1. Electron Flow
The release of electrons from the semiconductor material creates a flow of electricity, which can then be harnessed for various applications. This is the basic principle behind the generation of solar power using photovoltaic cells.
2.2. Direct Current Output
The electricity generated by photovoltaic cells is in the form of direct current (DC). This type of electricity is commonly used in electronic devices and can also be converted into alternating current (AC) for use in the electrical grid.
3. Applications of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are widely used in solar panels to generate electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. They are also used in small-scale devices like calculators and solar-powered gadgets.
3.1. Solar Panels
Photovoltaic cells are interconnected and encapsulated in solar panels to create larger arrays that can generate significant amounts of electricity. These panels can be installed on rooftops or in solar farms to power homes and businesses.
3.2. Consumer Electronics
Miniature photovoltaic cells are used in consumer electronics to provide power for devices such as watches, calculators, and outdoor solar lights. These small cells are efficient in converting sunlight into electricity for low-power applications.
In conclusion, photovoltaic cells work by harnessing the energy of sunlight to generate electricity through the photovoltaic effect. These cells are an essential technology in the field of renewable energy and have a wide range of applications in today’s world.

