Why Do We Use Semiconductors for Photovoltaics
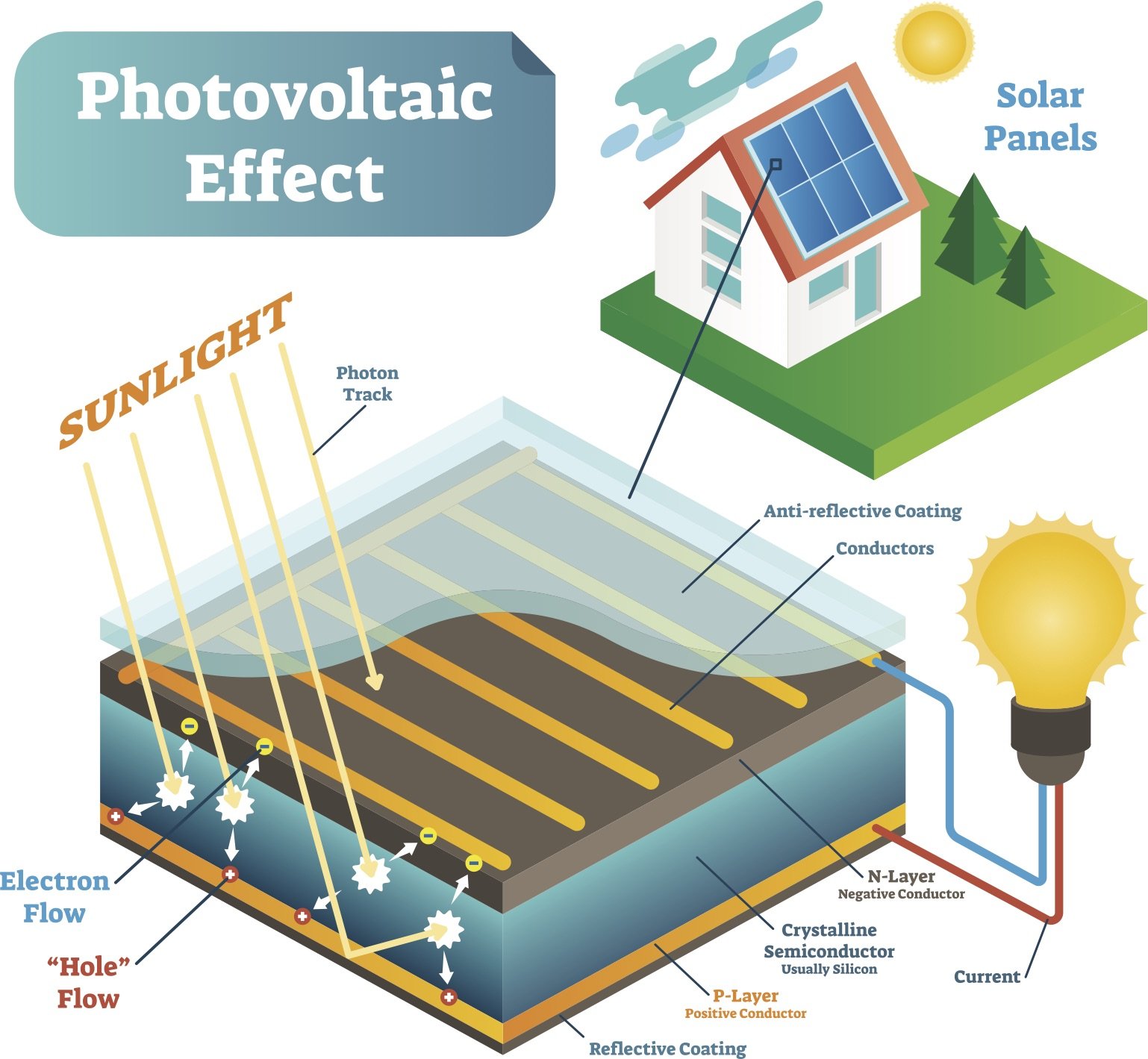
Photovoltaics, or the conversion of light into electricity, has become an increasingly important technology as the world shifts towards renewable energy sources. Semiconductors play a crucial role in photovoltaic devices, and understanding why we use them is key to unlocking the potential of solar power. In this article, we explore the reasons behind the use of semiconductors for photovoltaics.
The Nature of Semiconductors
1. Band Gap
Semiconductors have a unique property known as a band gap, which is the energy difference between the valence band and the conduction band. This band gap allows semiconductors to selectively absorb photons with specific energies, making them ideal for capturing solar energy. By adjusting the composition of semiconductors, researchers can tailor their band gaps to optimize their performance in photovoltaic applications.
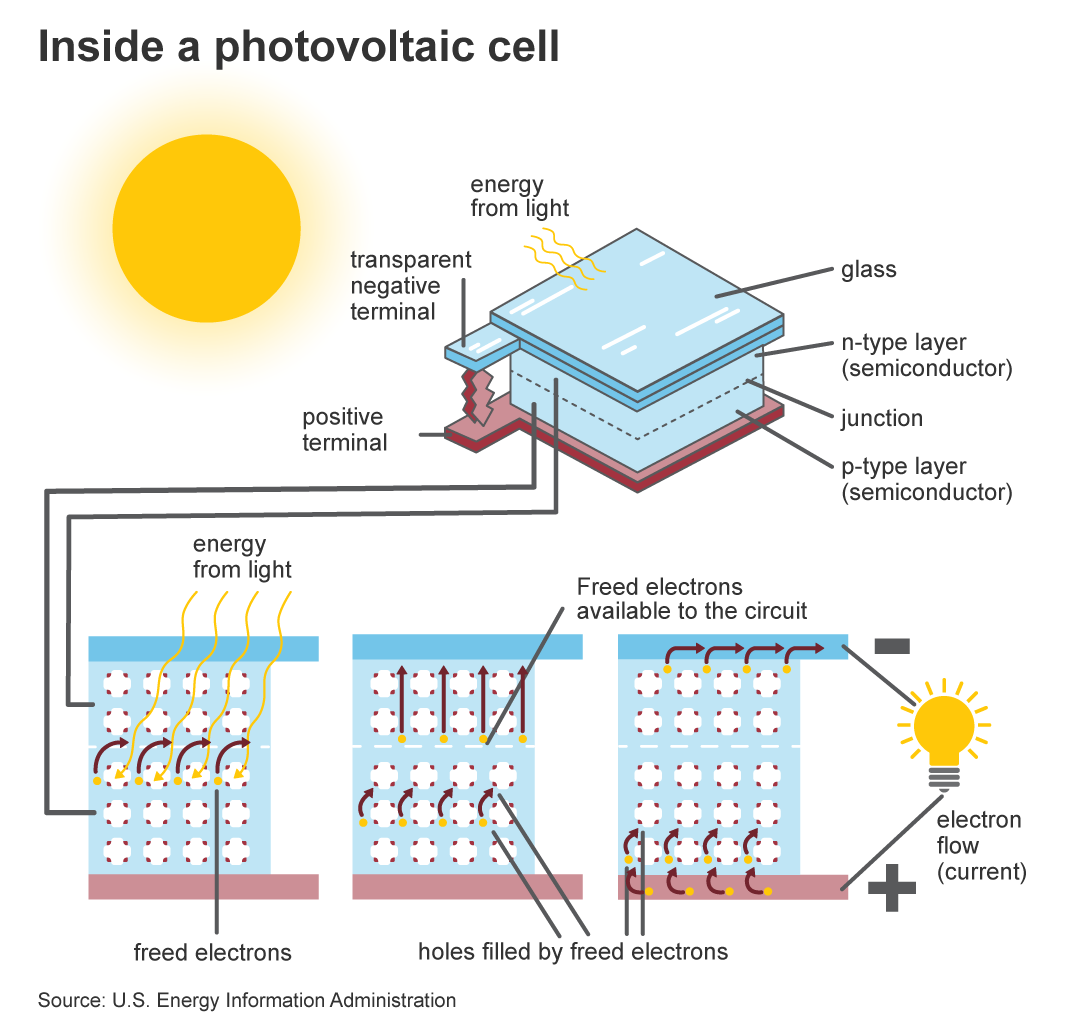
2. Electrical Conductivity
Another important characteristic of semiconductors is their ability to conduct electricity. When light is absorbed by a semiconductor, it can create electron-hole pairs, which can then be separated and collected as electrical current. This process forms the basis of solar cell operation and underscores the critical role of semiconductors in converting light into electricity.
Advantages of Semiconductors in Photovoltaics
1. Efficiency
Semiconductors allow for high efficiency in photovoltaic devices due to their ability to convert a large fraction of incoming sunlight into electrical energy. This is essential for making solar power economically competitive with traditional energy sources, as higher efficiency means lower overall costs for electricity generation.
2. Scalability
Semiconductors are highly scalable, making them suitable for a wide range of photovoltaic applications. Whether it’s a small rooftop solar panel or a large utility-scale solar farm, semiconductors can be tailored to meet the specific power output requirements, making them a versatile choice for solar energy generation.
3. Durability
Many semiconductor materials used in photovoltaic devices are durable and resistant to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature fluctuations. This durability ensures the long-term performance and reliability of solar panels, making them a viable investment for both residential and commercial applications.
Conclusion
Semiconductors are an essential component of photovoltaic technology, offering unique properties that enable the efficient conversion of sunlight into electricity. As the demand for solar energy continues to grow, the use of semiconductors in photovoltaics will play an increasingly important role in the transition to sustainable energy sources. Understanding the reasons behind their use is crucial for unlocking the full potential of solar power.
By leveraging the properties of semiconductors and continuing to advance their performance, the solar industry can continue to drive down costs and increase the adoption of renewable energy, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.

