The photovoltaic effect, also known as the solar cell effect, is the process through which a material generates an electrical current when exposed to light. This phenomenon occurs due to the interaction between light and the material’s electrons.
How does the photovoltaic effect occur?
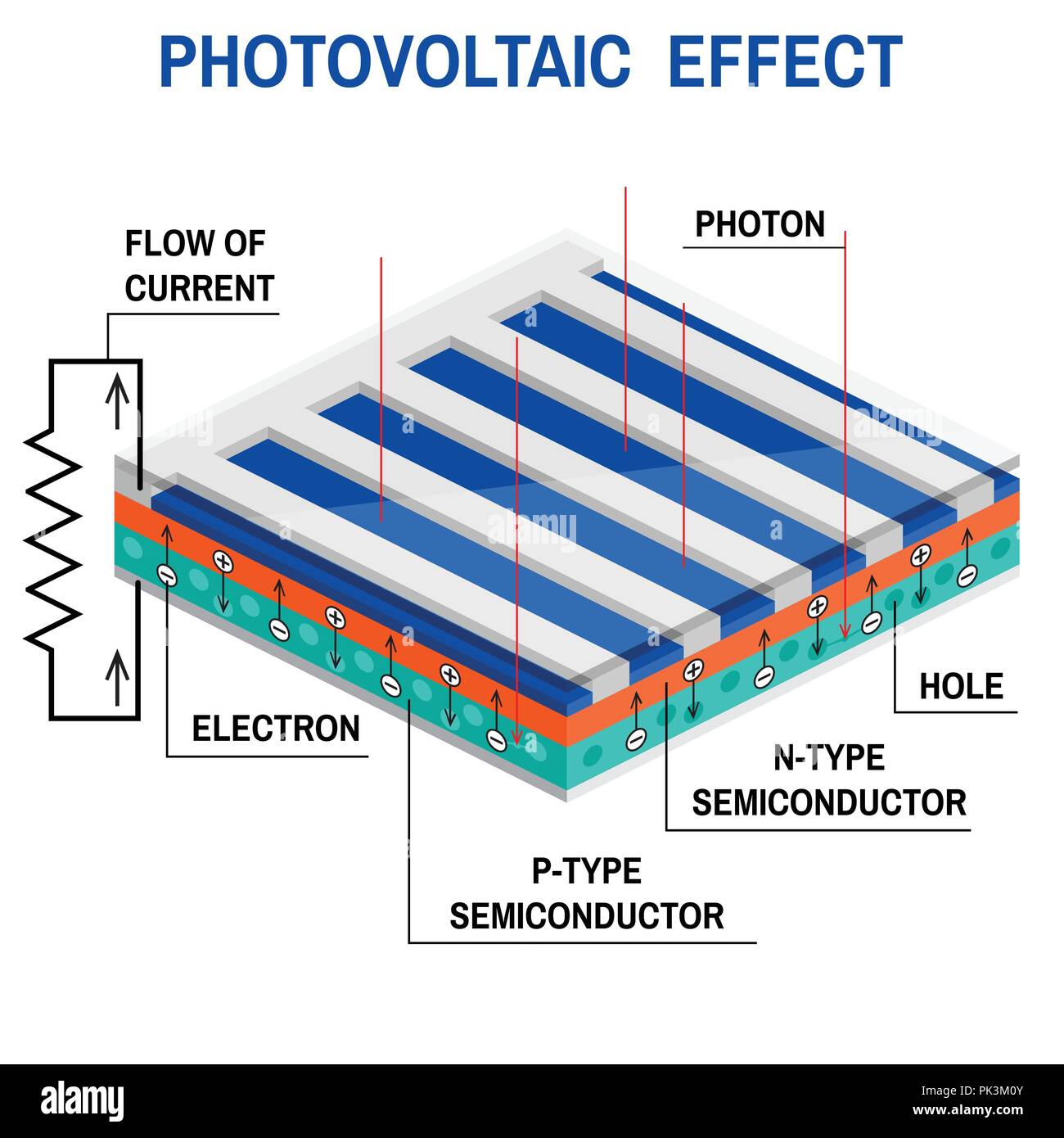
When light particles, called photons, hit the surface of a material, they transfer their energy to the material’s electrons. This energy causes the electrons to break free from their atomic bonds, creating electron-hole pairs. These pairs then move through the material, generating an electrical current.Key components of the photovoltaic effect
1. Absorption of light: The material used in photovoltaic cells must be capable of absorbing light across a wide range of wavelengths. This allows for efficient energy conversion. 2. Generation of electron-hole pairs: When a photon’s energy is transferred to an electron, it can overcome the material’s band gap, creating an electron-hole pair. 3. Separation of charges: Once the electron-hole pairs are generated, they need to be separated and directed to the electrical contacts of the photovoltaic cell to create a usable electrical current.Types of materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect
Various materials can exhibit the photovoltaic effect, but the most commonly used are semiconductors such as silicon, which is the primary material used in solar cells. Other materials, such as cadmium telluride and copper indium gallium selenide, are also used due to their ability to efficiently convert light energy into electrical energy.
The role of the p-n junction
In many solar cells, a p-n junction is created within the semiconductor material. This junction helps to separate the generated electron-hole pairs and direct them towards the electrical contacts, thus creating a flow of electricity.Applications of the photovoltaic effect
The photovoltaic effect has numerous practical applications, with the most notable being the generation of electricity from sunlight in solar panels. These panels can be used in both residential and commercial settings to offset traditional energy consumption and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.In conclusion, the photovoltaic effect occurs when light particles interact with a material, causing the generation of electron-hole pairs and the subsequent production of electrical current. This process is crucial for the generation of solar energy and has widespread applications in the field of renewable energy.

